Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway
Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway
|
Link:http://output.to/sideway/default.asp?qno=170300023 Windows 8.1 Knowledge Base Windows ReadyBoost
Microsoft Windows ReadyBoostReference:
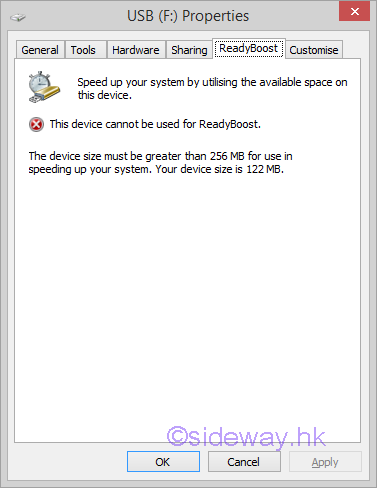
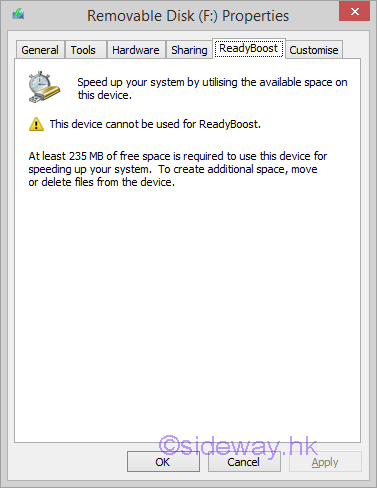
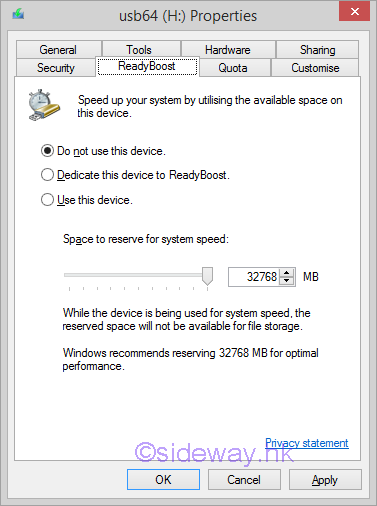
Windows ReadyBoost is a windows feature of using flash drives as a hard disk cache to improve disk read performance. Microsoft Windows ReadyBoostThe technology of ReadyBoost is designed as the secondary storage of the SuperFetch to provide fast, random, non-sequential reads. The technology of SuperFetch is making use of an algorithm to determine which files should be prefetched in a temporary cache. In general, the background SuperFetch tasks preload those most used files in unused RAM so that programs can be loaded faster from RAM than to be accessed from the hard disk every time. However, adding of RAM to a PC is usually limited by the available physical memory slots on the motherboard, or the addressing capability of the motherboard and operating system. Instead of caching all data in RAM, some small disk transactions can also be handled by flash memory to improve random, non-sequential disk read performance. An external type of flash memory storage is therefore used as the secondary storage of the SuperFetch, named ReadyBoost, to provide a more flexible way of using flash memory as disk cache. USB Flash Drive for ReadyBoostThe ReadyBoost supported external storage can be USB thumb drives, SD cards, and CF cards etc. In order to ensure the performance of disk cache in using with ReadyBoost, Windows will automatically check the performance characteristic of the storage device for ReadyBoost compatibility. The minimum requirements of ReadyBoost storage are
If the device does not meet the minimum requirements, Windows will disable ReadyBoost for that device. 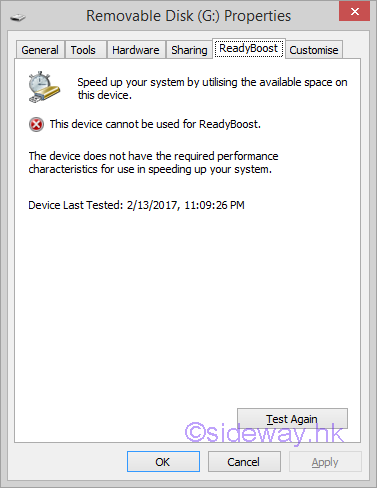 Features of ReadyBoostReadyBoost will create a empty full size disk cache file named ReadyBoost.sfcache in the root of the ReadyBoost flash drive, cached content will be filled later. The ReadyBoost performance can be monitored using the Computer Management console by adding the ReadyBoost Cache counters under the System Tools\Performance\Monitoring Tools\Performance Monitor tool. These counters display how much of the cache is currently being used and when the cache is read from or written to. All files in the cache are encrypted using 128-bit AES if the flash storage device is removable, but hardware manufacturers can choose to disable encryption on internal, non-removable ReadyBoost devices. Since the ReadyBoost only caches a copy of the files in the flash drive for improving disk reading, the flash drive can be removed at any time without affecting the operation of computer. In general, ReadyBoost can only provide significant performance improvement on a computer with a slow hard disk drive. Computers with a primary hard disk Windows Experience Index (WEI) subscore lower than 4.0 will see the most significant improvements. The flash storage must be connected to a fast bus interface in order to achieve the minimum throughput, that is USB2,0 or above, Typically, USB memory card readers are not sufficiently fast. However, connecting flash memory to an internal memory card reader might provide sufficient performance. Finally, a flash storage usually can provide fast, random, non-sequential reads over traditional hard disk. While the performance gain in sequential read speed is less significant. Computers with fast hard disks, such as 7,200- or 10,000-RPM hard disks, might realize minimal performance gains because of the already high disk I/O during sequential reads. But the latency caused by moving the drive head to another different disk sector during non-sequential reads will reduce the disk read performance of traditional hard disk. Therefore, ReadyBoost with minimum requirement can usually read faster from the cache during non-sequential reads. In other words, when disk reading from an SSD, Windows will disables ReadyBoost for that drive because ReadyBoost will not provide a performance gain. Links of ReadyBoost
|
Sideway BICK Blog 23/03 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||