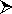|
Link:http://output.to/sideway/default.asp?qno=120200065 Equilibrium in Three Dimensions
Equilibrium in Three Dimensions
In general, the conditions for the equilibrium of a rigid body
is.
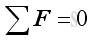 and and
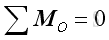
For three dimensional problems, the resultant can be decomposed
into three components. Imply
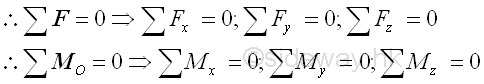
Three translational and three rotational motion are
needed for determining a three
dimensional structure is in static equilibrium state or not.
In other words, the possible forces and moments
due to an applied action or a
reaction in a three dimensional structure are three rectangular forces and
three rectangular moments, or one resultant force and one moment in space.
Since there are only
six equations obtained from the equilibrium
equations of a rigid
body in three dimenstion, no more than six unknowns can be determined by the
system of six equations.
Reactions at Supports and Connections
In order to construct the free body diagram for analysing the equilibrium of
rigid body in three dimensions, the types of reactions at supports and connections
should be evaluated first.
The types of reactions at supports and connections can be divided into three
types:
-
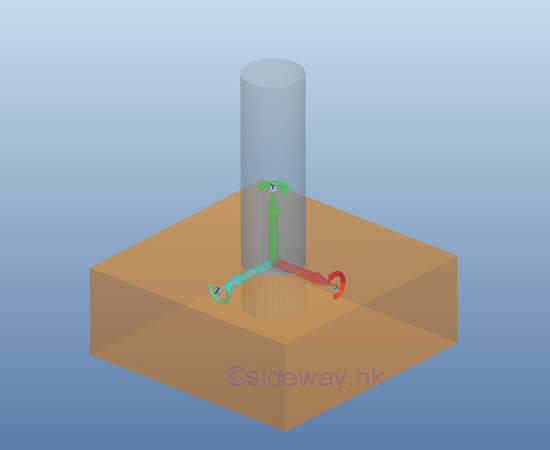
Reactions equivalent to
three force components and three couple components
For a fixed support, no translational motion and rotation motion is allowed for
the free body to move and thus the free body is fully constrained.
-
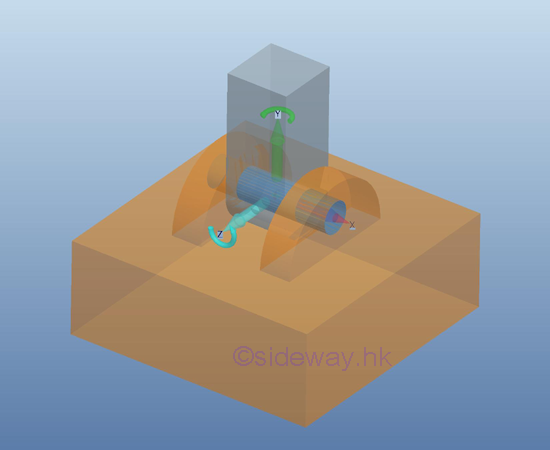
Reactions equivalent to three force components and two couple components
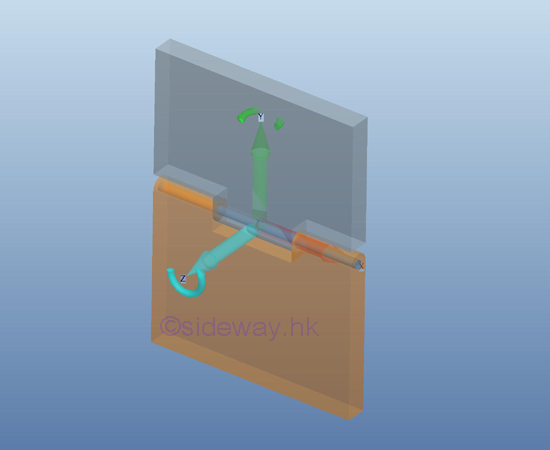
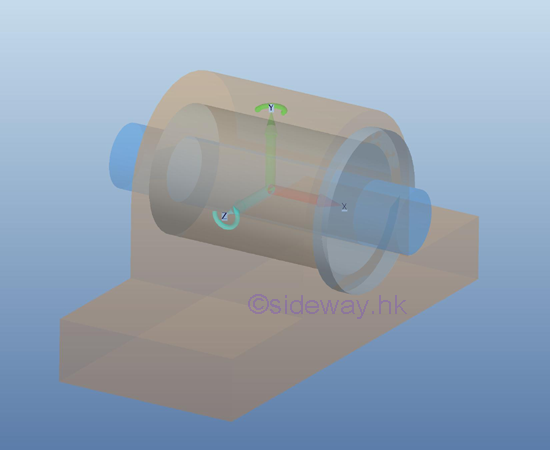
For
an axial thrust and radial load support or connection, the rotational motion in
one dimension is enabled by equipping with a fictionless hinge or pin, only two couple is reacted by the support
or connection on the free body. But, the translational motion is stopped by
the reaction force of the hinge support.
However, when using this type of support or connection in the design, the other
two couples may not always exist in normal operation.
-
Reactions equivalent to three force components and one couple component
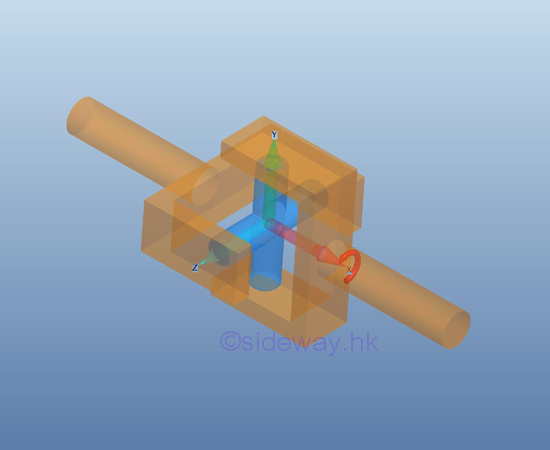
For
an universal joint, the rotational motion in two dimensions is enabled by
equipping with a pair of hinges oriented at 90 degree to each other, only one couple is reacted by the support
or connection on the free body. But, the translational motion is stopped by
the reaction force of the hinge support.
-
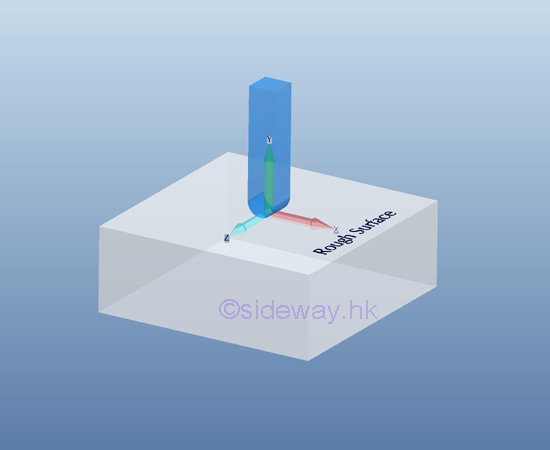
Reactions equivalent to three force components
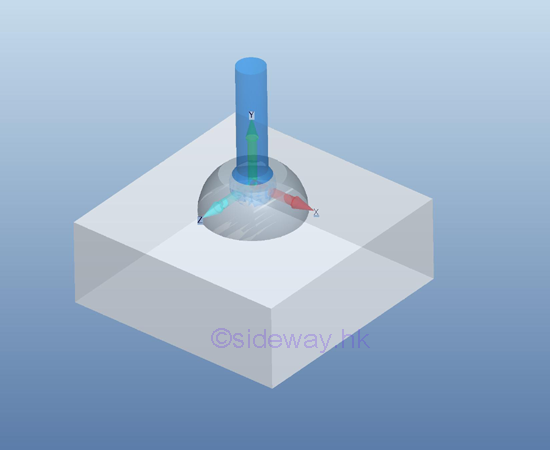
For
a ball and socket joint, the free rotational motion in three dimensions is
enabled by equipping with a ball in a frictionless socket, or a free end on a
rough surface, no couple is reacted by the support
or connection on the free body. But, the translational motion is stopped by
the reaction force of the socket support or the friction force generated by the
rough surface.
-
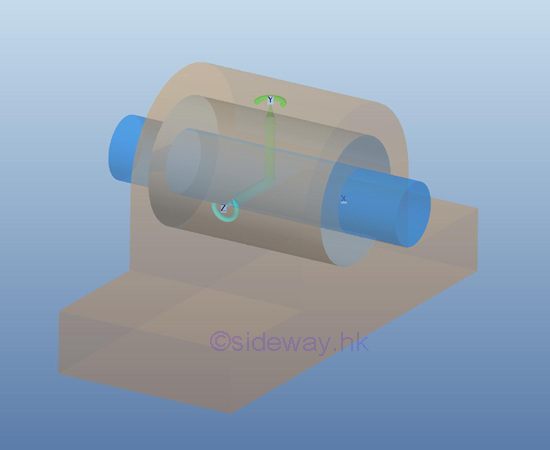
Reactions equivalent to two force components and two couple components couple components
For
a radial load support or connection, the rotational motion in one dimension is
enabled by equipping with a fictionless hinge or pin, only two couple is reacted by the support
or connection on the free body. Because there is no axial thrust, the axis is
free to move on the axial direction, and only two translational motions are stopped by the reaction force of the hinge support.
However, when using this type of support or connection in the design, the other
two couples may not always exist in normal operation.
-
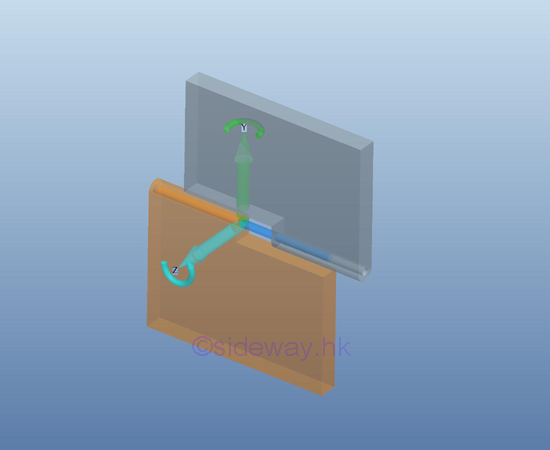
Reactions equivalent to two force components
For
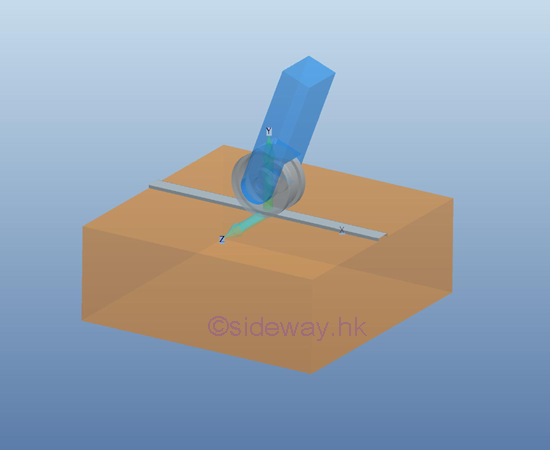
a free roller support or connection, the rotational motion in one dimension is
enabled by equipping with a roller with fictionless hinge or pin on rough
surface or a rail, and the free rotational motion on other two dimensionsuonly
two couple is allowed by the free end design. And therefore there is no couple reacted by the support
or connection on the free body. Because there is a roller, the free translation
is allowed along the rolling direction of the roller, and only two translational motion
are stopped by the reaction force of the roller support on the rought surface or
the rail.
-
Reactions equivalent to one force components
-
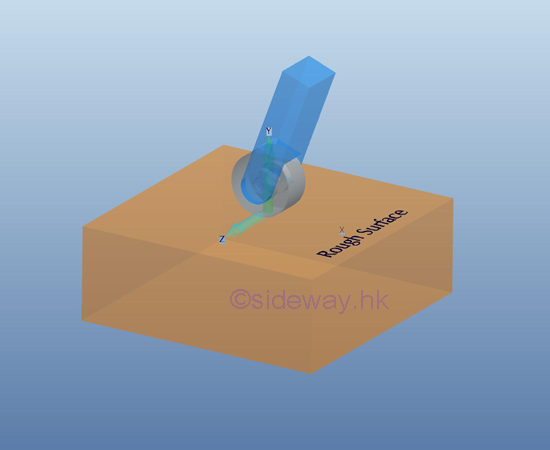
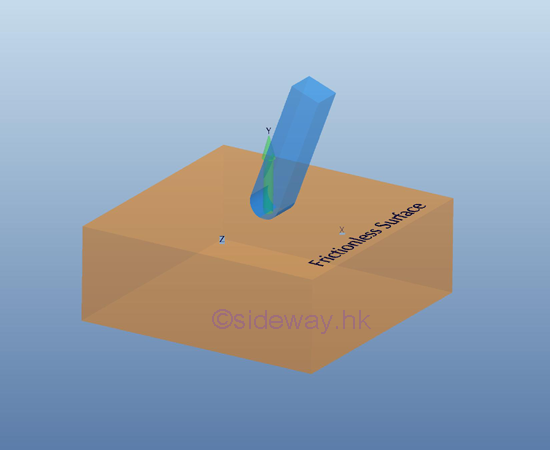
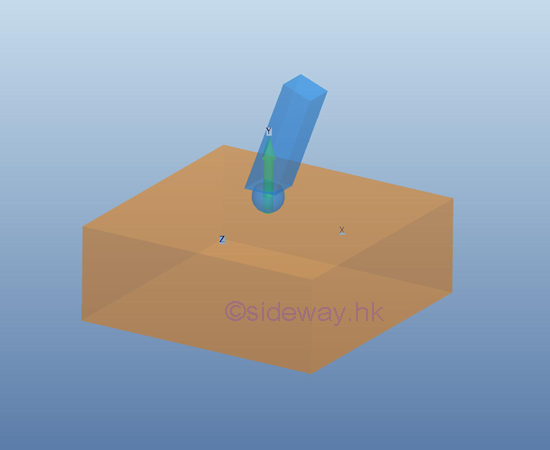
For a ball support or connection
For
a ball support, simulart to the ball and socket joint, the free rotational motion
in three dimensions is enabled by equipping with a free spherial end on a
surface as a point contact or a free end on a frictionless surface, no couple is reacted by the support
or connection on the free body. Besides, the two translational motions in
horizontal or lateral and longitudinal direction also also free to motion. Only
the translational motion in vertial or normal direction is stopped by the reaction force of the supporting
surface.
-
For
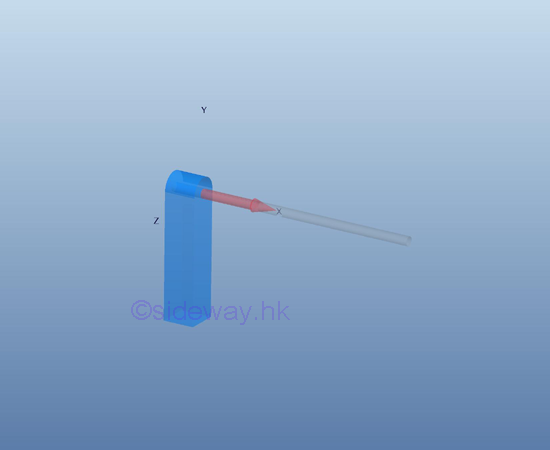
free short cable support or connection
For a cable, the only possible reaction force is the tension of the cable. Therefore
a free short cable provides only one constraint along the cable to the
free body.
|
|
 Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway
Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway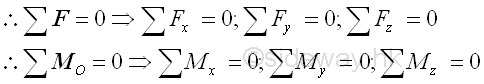
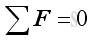 and
and