Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway
Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway
|
Link:http://output.to/sideway/default.asp?qno=121000009 Moment of Inertia of Composite Area Second Moment of Composite AreaBy definition, second moment of an area about an axis is equal to the summation of the products of the square of the distance between the elemental area and the reference axis, and the elemental area over an area. If these elemental areas can be grouped into known component areas A1, A2, A3, ...., the second moment I of the composite area A with respect to an axis can be obtained by the summation of the second moments, I1, I2, I3, .... of these component areas A1, A2, A3, ...., about the same reference axis respectively. Imply 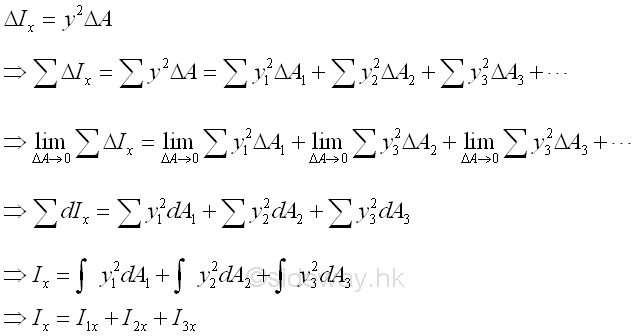
The component area of a composite area is represented by a positive area while a hollow area is represented by a negative area. Second Moment of Circular Area Example 1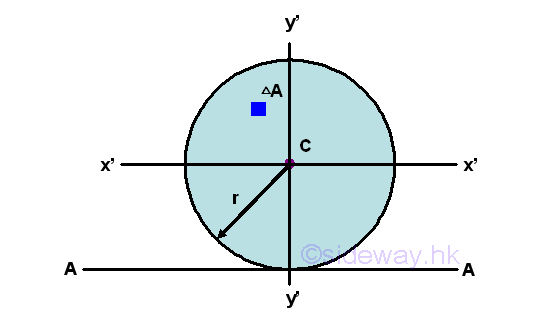
Since a circular area can be considered as two semi-circular area or four quarter-circular area, the second moment of a circular area about the centroidal axis x' can be expressed in terms of the second moments of semi-circular areas or quarter-circular areas. As for two semi-circular areas, 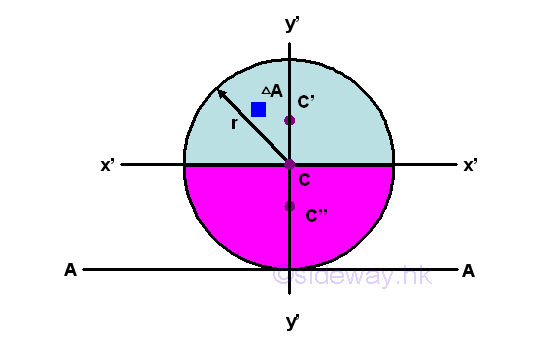
Because of the square of the distance from the reference axis x', the second moments of the two semi-circular areas about axis x' are the same on two opposite sides of the reference axis. Imply 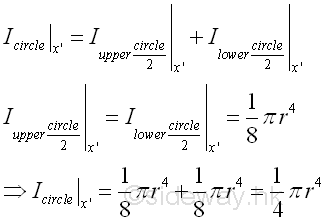
As four quarter-circular areas, 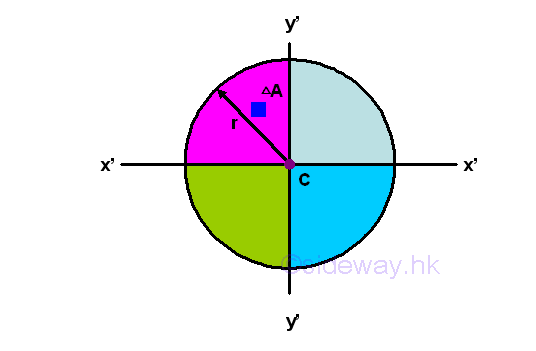
Because of the square of the distance from the reference axis y', the second moments of the four quarter-circular areas about axis y' are the same on two opposite sides of the reference axis. Imply 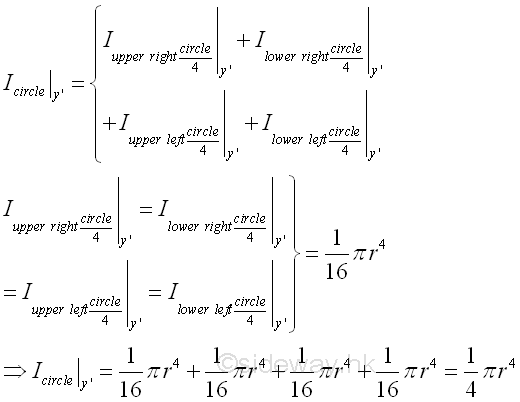
Besides, the polar moment of an area can also be obtained similarly. Because of the square of the distance from the reference pole C, the second moments of the four quarter-circular areas about the pole C are the same. Imply 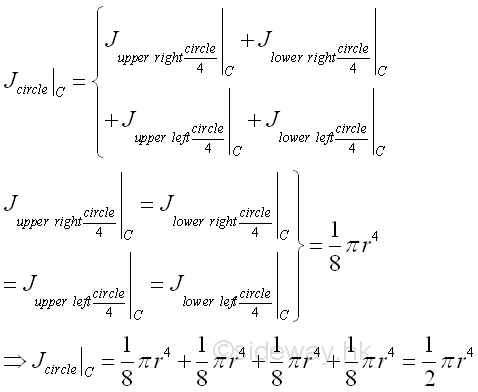
Second Moment of Circular Area Example 2
In example 1, the reference axis x' of the circular area is the same axis used in defining the second moment of the semi-circular areas and the quarter-circular areas, the second moments of the component areas can be added directly. But if the reference axis is changed to axis A, each second moment of a component area should be transfered to the desired axis A by parall-axis theorem or by calculation before adding. As for two semi-circular areas, 
Since the two second moments of the two semi-circular areas are about the axis x', the two second moments of the two semi-circular areas should be transfered to the axis A before adding accordingly. Imply 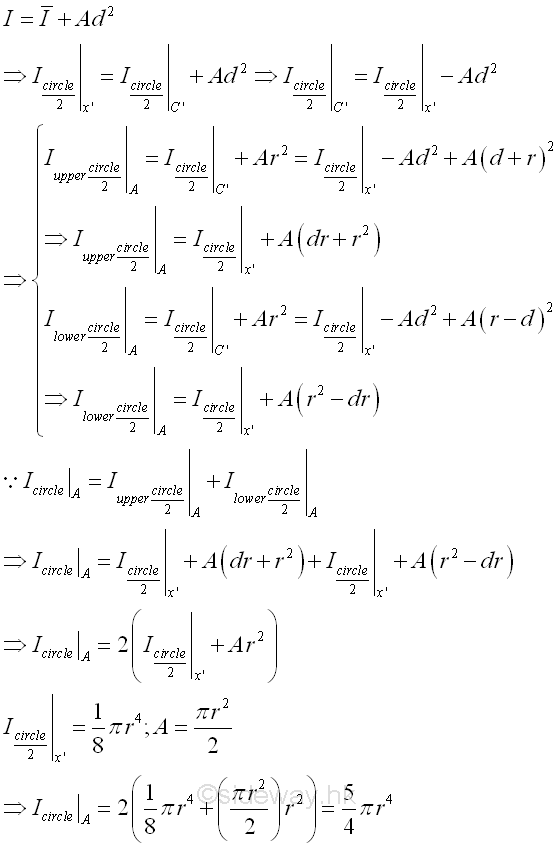
Negative Area of a composite area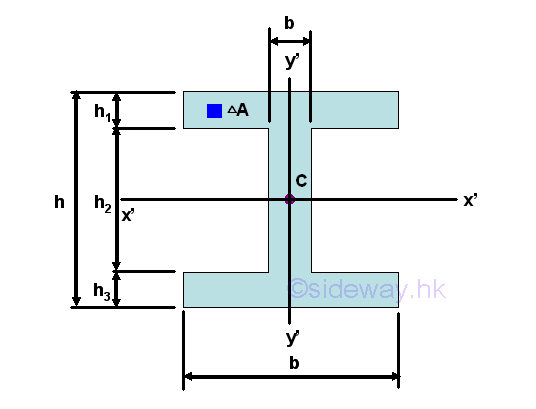
Sometimes, an empty area in a composite area can also be considered in calculating the second moment of a composite area by changing the sign of the empty area to negative before adding. And therefore the empty component area of a composite area is also called negative area. For example, the second moment of an I-beam area starting with all positive components. Imply 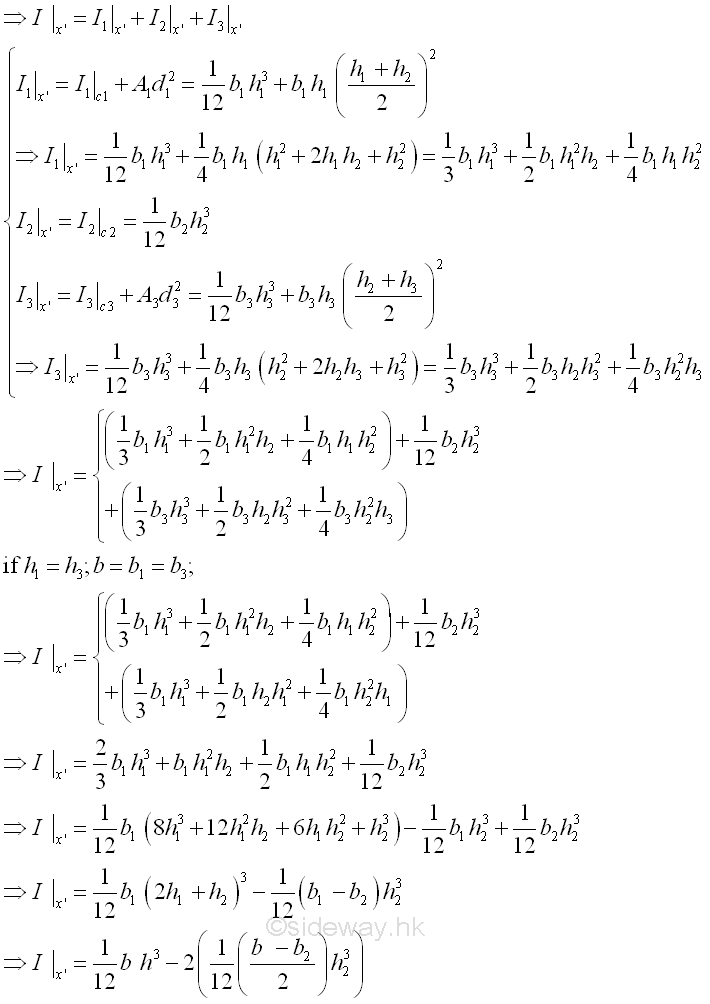
Therefore, the second moment of an I-beam area starting with positive and negative components. Imply 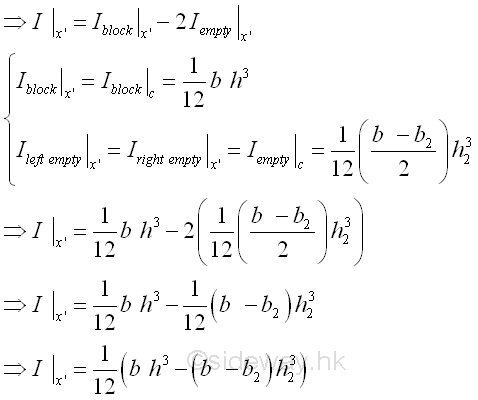
Radius of gyration of composite areaUnlike the polar radius of gyration, kO which can be obtained using the two rectangular radius of gyration, kx and ky only, the radius of gyration of a composite area can not be obtained using the radii of gyration of all component areas of a composite area only. The radius of gyration of a composite area can be determined by the second moment of the composite area and the area of the composite area directly or making use of the radii of gyration of all component areas of a composite area together with the areas of the component areas of a composite area. Imply 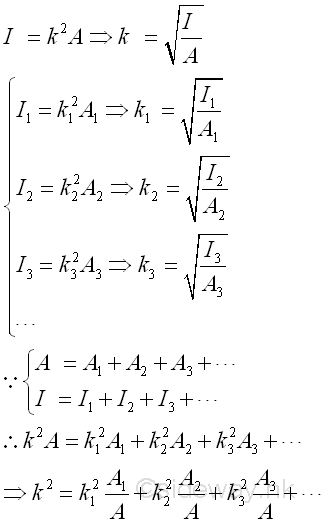
Link:http://output.to/sideway/default.asp?qno=121000008 Moment of Inertia of an Area Second Moment of An Area of Geometric ShapeThe second moment of an area of a geometric shape can be determined by integration or the parallel-axis theorem. Imply 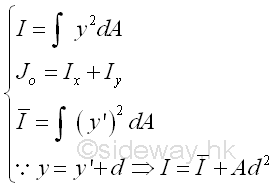
Moment of Inertia of AreasSecond Moment of Area of Semi-circleSecond Moment about x by Double Integration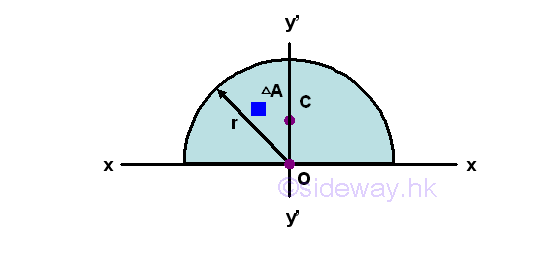
The second moment of an area of a semicircle about the axis x is 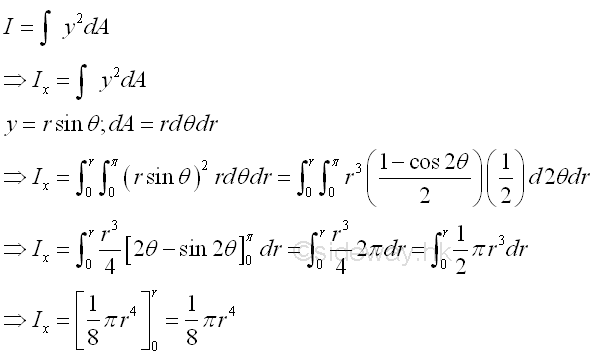
Second Moment about y' by Double IntegrationThe second moment of an area of a rectangle about the centroidal axis y' is 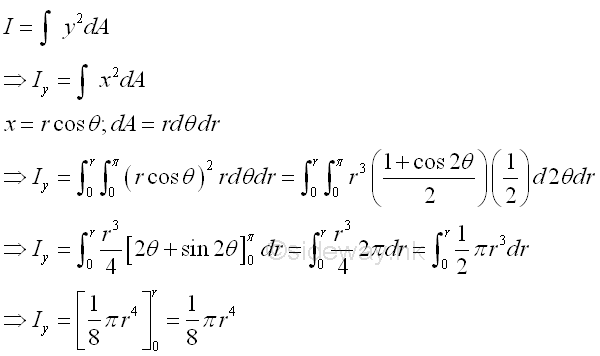
Polar Moment about O from Rectangular Moments of InertiaThe polar moment of an area of a rectangle about the center O is 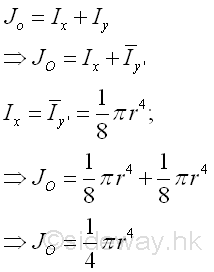
Second Moment of Area of Quarter-circleSecond Moment about x by Double Integration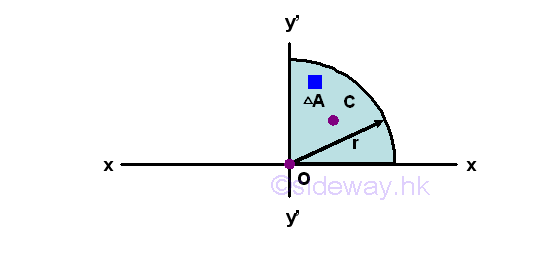
The second moment of an area of a semicircle about the axis x is 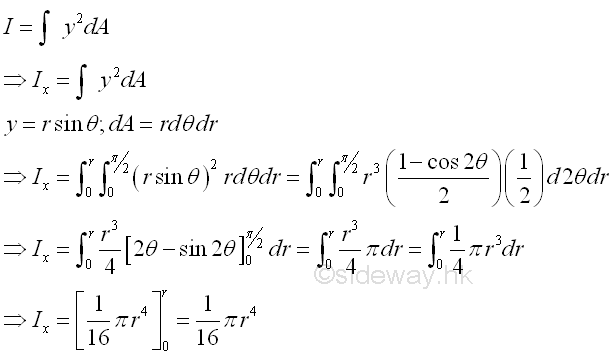
Second Moment about y' by Double IntegrationThe second moment of an area of a rectangle about the centroidal axis y' is 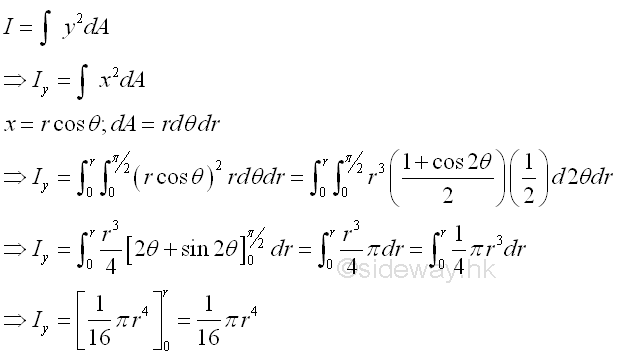
Polar Moment about O from Rectangular Moments of InertiaThe polar moment of an area of a rectangle about the center O is 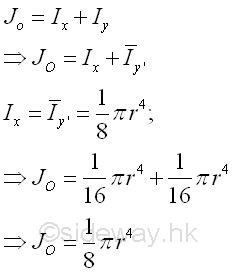
Second Moment of Area of EllipseSecond Moment about x' by Double Integration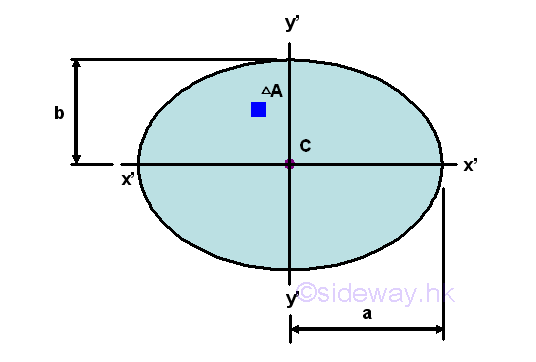
The second moment of an area of a ellipse about the centroidal axis x' is 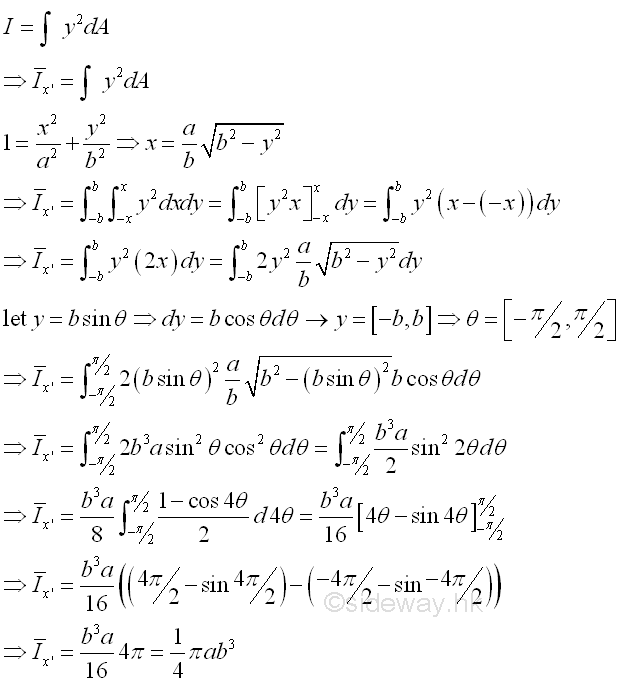
Second Moment about y' by Double Integration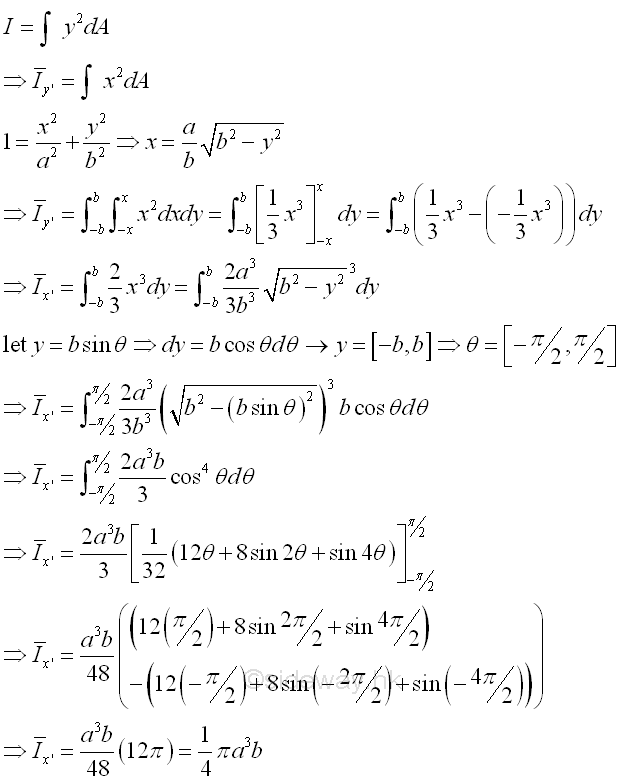
Polar Moment about C from Rectangular Moments of InertiaThe polar moment of an area of a circle about the centroid C is 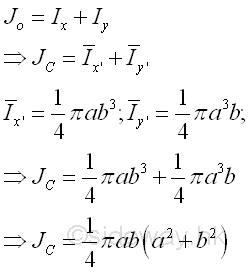
|
Sideway BICK Blog 18/10 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||