Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway
Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway
|
Link:http://output.to/sideway/default.asp?qno=180300014 Script, Scripting Language, VBScript elements, Server-Side VBScript Function, Math Function, Derived Math Function
VBScript Derived Math FunctionsSome common non-intrinsic math functions can be derived from the intrinsic vbs math functions Mathematical ConstantsExamples of mathematical constants Constant πASP VbScript Command: HTML Web Page In-line Output: π≈pi=4*Atn(1)=3.14159265358979 Constant eASP VbScript Command: HTML Web Page In-line Output:
e=e^1≈Exp(1)=2.71828182845905 Trigonometric FunctionsExamples of trigonometric functions 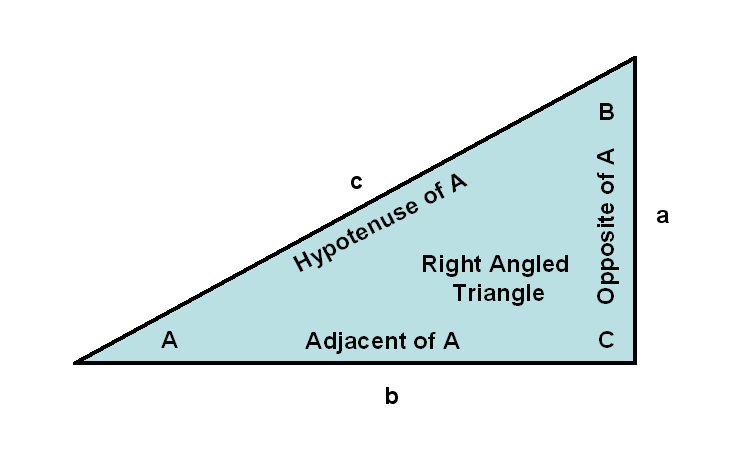
Function (let c=1)Mathematical EquationDerived equivalent
Secant function, sec(A)=c/bsec(A)=1/cos(A)1/Cos(A)
Cosecant function, csc(A)=c/acsc(A)=1/sin(A)1/Sin(A)
Cotangent function, cotan(A)=b/acotan(A)=1/tan(A)1/Tan(A)
Inverse sine function, A=arcsin(a/c)= arcsin(a)A=arcsin(a/c)=arctan(a/b)= arctan(a/(c^2-a^2)^0.5)Atn(a/Sqr(-a*a+1))
Inverse cosine function, A=arccos(b/c)= arccos(b)A=arccos(b/c)=arccotan(b/a)= π/2-arctan(b/(c^2-b^2)^0.5)= arctan(-b/(c^2-b^2)^0.5)+π/2Atn(-b/Sqr(-b*b+1))+2*Atn(1)
Inverse secant function, A=arcsec(c/b)A=arcsec(c/b)=π/2-arccsc(c/b)2*Atn(1)–Atn(Sign(x)/Sqr(x*x–1))
Inverse cosecant function, A=arccsc(c/a)A=arccsc(c/a)=arctan(a/b)= arctan(a/(c^2-a^2)^0.5)= arctan(Sign(c/a)/((c/a)^2-1)^0.5)Atn(Sgn(c/a)/Sqr((c/a)*(c/a)–1))= Atn(Sign(x)/Sqr(x*x–1))
Inverse cotangent function, A=arccotan(b/a)A=arccotan(b/a)= π/2-arctan(b/a)2*Atn(1)-Atn(b/a)= 2*Atn(1)-Atn(x)
Hyperbolic FunctionsExamples of hyperbolic functions
FunctionMathematical EquationDerived equivalent
Hyperbolic sine sinh(x)(e^x-e^-x)/2(Exp(x)–Exp(-x))/2
Hyperbolic cosine cosh(x)(e^x+e^-x)/2(Exp(x)+Exp(-x))/2
Hyperbolic tangent tanh(x)(e^x-e^-x)/(e^x+e^-x)(Exp(x)–Exp(-x))/(Exp(x)+Exp(-x))
Hyperbolic secant sech(x)2/(e^x+e^-x)2/(Exp(x)+Exp(-x))
Hyperbolic cosecant csch(x)2/(e^x-e^-x)2/(Exp(x)–Exp(-x))
Hyperbolic cotangent coth(x)(e^x+e^-x)/(e^x-e^-x)(Exp(x)+Exp(-x))/(Exp(x)–Exp(-x))
Inverse hyperbolic sine arcsinh(x)ln(x+(x^2+1)^0.5)Log(x+Sqrt(x*x+1))
Inverse hyperbolic cosine arccosh(x)ln(x+(x^2-1)^0.5)Log(x+Sqrt(x*x–1))
Inverse hyperbolic tangent arctanh(x)ln((1+x)/(1-x))/2Log((1+x)/(1–x))/2
Inverse hyperbolic secant arcsecH(x)ln(1/x+(1/x^2-1)^0.5)= ln((1+(1-x^2)^0.5)/x)Log((Sqr(-x*x+1)+1)/x)
Inverse hyperbolic cosecant arccsch(x)ln(1/x+(1/x^2+1)^0.5)= ln((1+Sign(x)*(1+x^2)^0.5)/x)Log((Sgn(x)*Sqr(x*x+1)+1)/x)
Inverse hyperbolic cotangent arccoth(x)ln((x+1)/(x-1))/2Log((x+1)/(x–1))/2
Logarithm FunctionsExamples of logarithm functions Logarithm FunctionsASP VbScript Command: HTML Web Page In-line Output:
Log(x): The natural logarithm of x has the number e (≈ 2.718) as its base. Log(x):Logarithm of x to base e: e=Exp(1)=2.71828182845905 ln_e=log(e)=1 Log10(x): The common logarithm of x has the number 10 as its base. Log10(x):Logarithm of x to base 10: ten=10^1=10 log10_10=log(10)/log(10)=1 hundred=10^2=100 log10_100=log(100)/log(10)=4.60517018598809/2.30258509299405=2 LogN(x): The logarithm of x has the number N as its base. LogN(x):Logarithm of x to base N=Log(x)/Log(N) Sources |
Sideway BICK Blog 14/03 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Copyright © 2000-2020 Sideway . All rights reserved Disclaimerslast modified on
26 January 2013