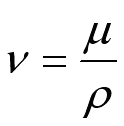Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway
Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway
|
Link:http://output.to/sideway/default.asp?qno=100100005 Viscosity Fluid PropertiesViscosityViscosity or Dynamic Viscosity is used to describe the fluidity property or the internal resistance of a fluid to motion. From experimental observation, when a fluid flows over a solid surface, it comes to a complete stop at the surface and sticks on it. This is known as the no-slip condition and all liquids and gases satisfy this condition. When considering a hypothetical experiment in which fluid is located between the small gap of two parallel plates. By fixing the bottom plate at rest and moving the upper plate at a constant velocity, the fluid deforms continuously under the shear force. 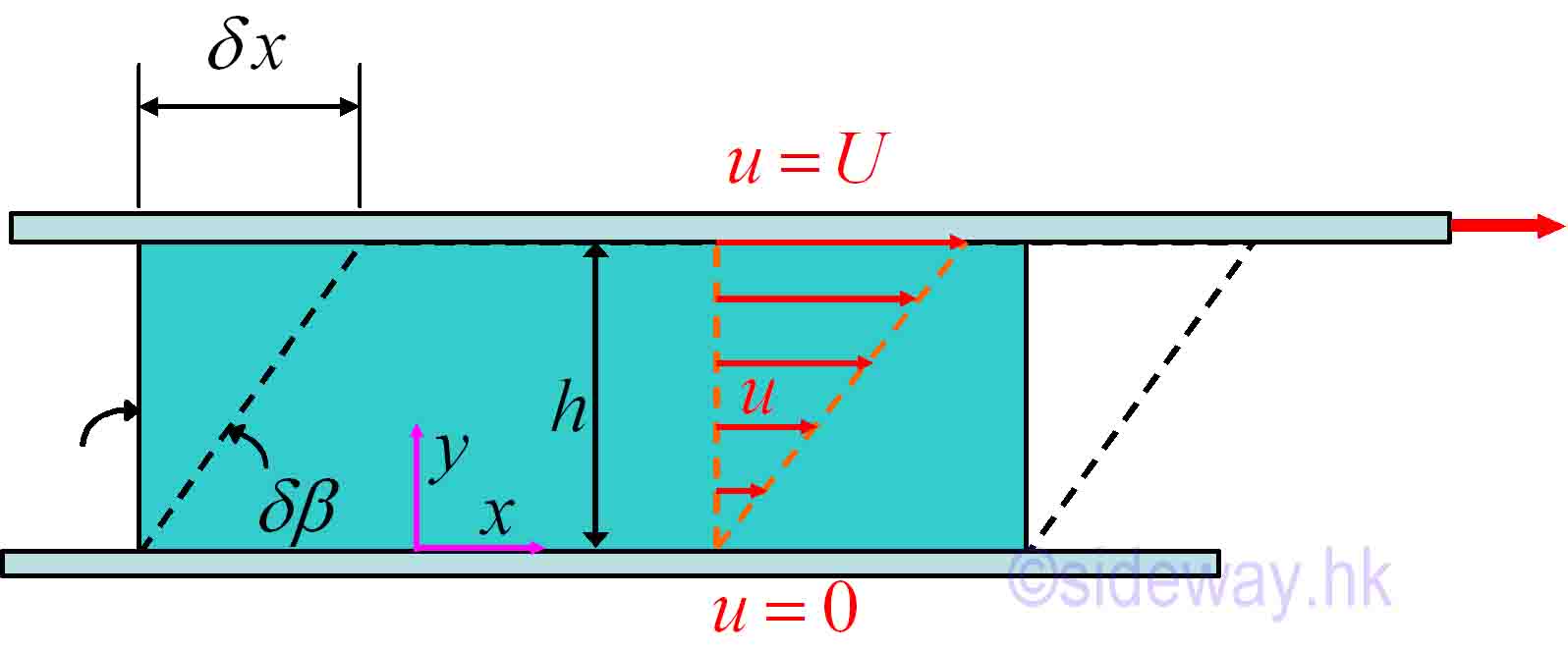
Because of the no-slip condition, the fluid contacts with the bottom fixed plate
has a zero velocity, while the fluid contacts with the upper moving plate moves
with the same upper plate velocity. As
For steady laminar flow, the velocity profile of the flow varies linearly away
from the fixed plate, i.e.
For a small time increment
From experimental results, the rate of shearing strain
Fluids with shearing stress linearly proportion to the rate of shearing strain
that can be described by a simple constant are called Newtonian fluids,
The ratio of dynamic viscosity to density usually appears and is named as
kinematic viscosity, i.e.
|
Sideway BICK Blog 25/01 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
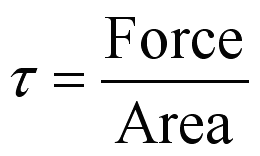 ,
the fluid deformation caused by the applied force to the moving plate is due to
the shearing stress.
,
the fluid deformation caused by the applied force to the moving plate is due to
the shearing stress. 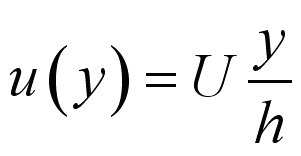 .
The velocity gradient is then equal to
.
The velocity gradient is then equal to
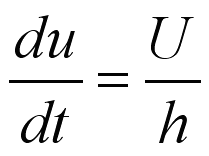 .
.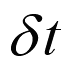 , the
upper plate will travel
, the
upper plate will travel
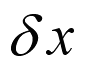 with
constant velocity
with
constant velocity
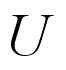 ,
therefore the shear strain equals to
,
therefore the shear strain equals to
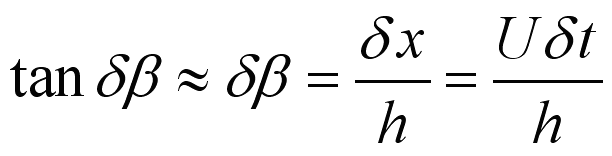 .
By rearrangement,
.
By rearrangement,
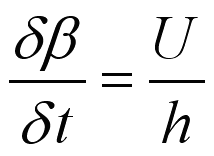 , imply
the rate of shearing strain due to the shear stress is
equals to
, imply
the rate of shearing strain due to the shear stress is
equals to
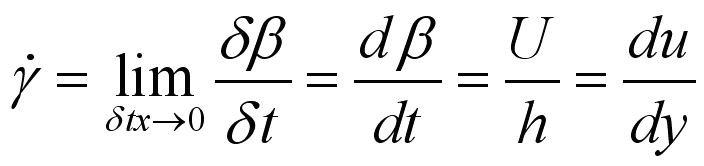
 is directly proportional
to the shear stress
is directly proportional
to the shear stress
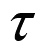 . i.e
. i.e
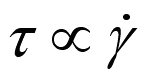 or
or
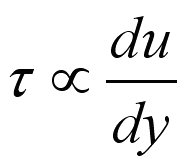 .
For some common fluid, the constant of proportionality is called the viscosity
of the fluid and expressed as
.
For some common fluid, the constant of proportionality is called the viscosity
of the fluid and expressed as
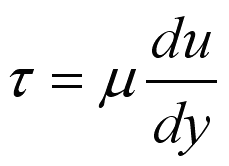 .
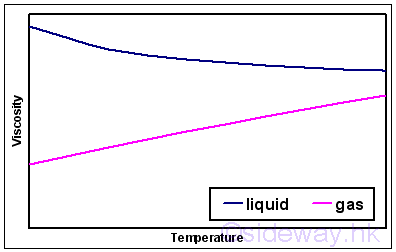
Every fluid has its own value of viscosity and the value is also highly
depending on temperature. And the viscosity of liquid decreases with the
temperature i.e
.
Every fluid has its own value of viscosity and the value is also highly
depending on temperature. And the viscosity of liquid decreases with the
temperature i.e
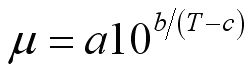 ,
while the viscosity of gas increases with temperature. i.e.
,
while the viscosity of gas increases with temperature. i.e.
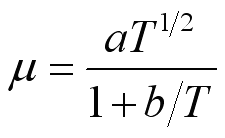
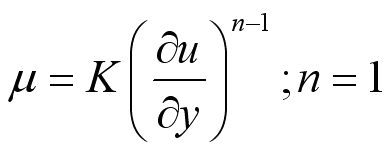 .
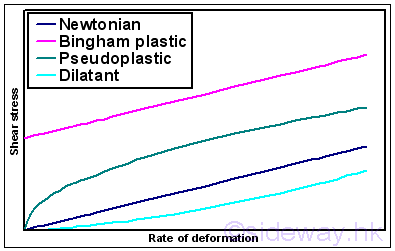
Non-Newtonian fluid, like Bingham plastic, Pseudoplastic and Dilatant cannot be
described by a single constant value of viscosity. i.e.
.
Non-Newtonian fluid, like Bingham plastic, Pseudoplastic and Dilatant cannot be
described by a single constant value of viscosity. i.e.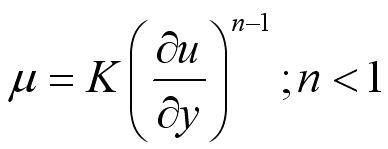 ;
;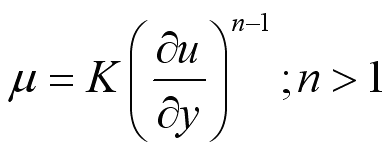 .
.