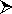Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway
Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway
|
Link:http://output.to/sideway/default.asp?qno=120300021 Distributed Force Distributed Force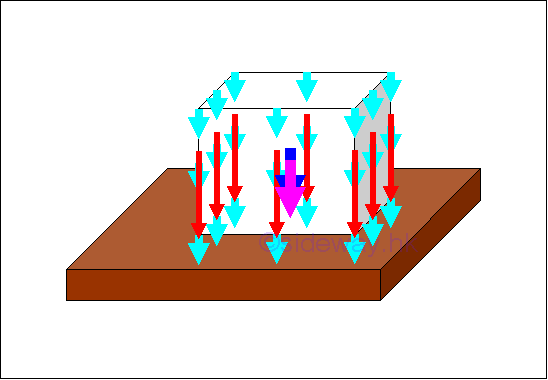
A force acting on a point along a single line in space is a concentrated force. A concentrated force is the mathematical idealization of forces in practical problems, in which all forces are either body forces acting over a volume or surface forces acting over an area. These types of forces are called distributed forces which are either distributed over a specific volume or spread out over a specific area. Through system of forces transformation, the distributed forces can be represented by a concentrated force. Body Force: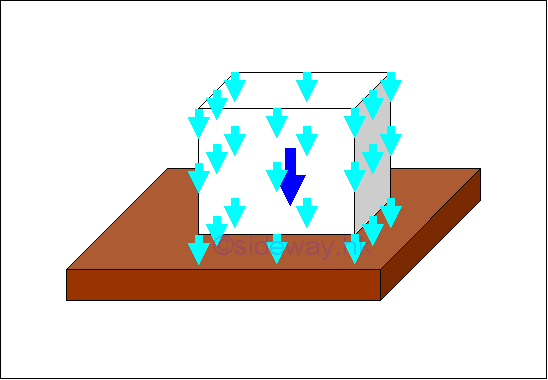
In static mechanic, a body force is the attraction force exerted by the earth on a rigid body. The attraction force is called the force of gravity or in general, the weight of the rigid body. The force of gravity acts on each of the particles of the entire body. Therefore the gravitational forces of a body can be represented by numbers of small gravitational forces distributed over the body volume. In mathematical idealization, the gravitational force of the body is represented by a resultant force acting on the center of gravity of the body as the weight of the body. The center of gravity of a body is related to the gravitation attraction, density and shape of the body. For an uniform gravitational force field, the center of mass of a body is equal to the center of gravity of a body. And in practical problems, the center of gravity is sometimes also refered to the center of mass. For a homogeneous body with constant mass density, the centroid of the shape of a body is equal to the center of gravity. Imply 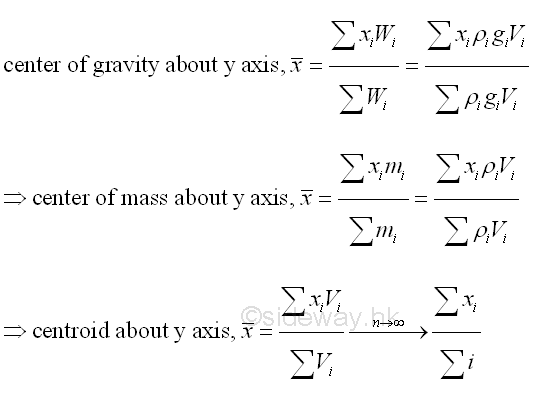
Distributed Load: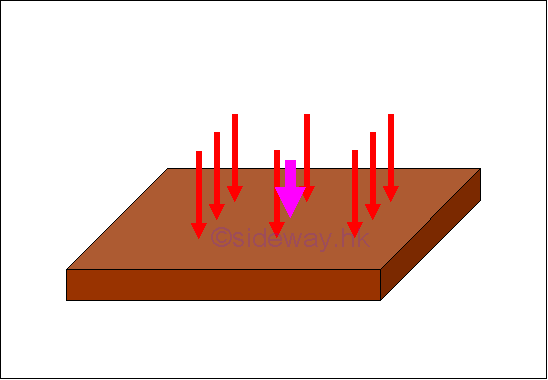
Similarly, many mechanical structures are subjected to distributed loads spread out over a specific area rather than concentrated loads in static mechanic. However, an equivalent normal concentrated force is often used to represent the applied distributed loads spread out over a specific area when solving practical problems. For an uniform distributed load, a load of constant magnitude is applied over a specific area. The resultant of these distributed loads can be represented by a normal concentrated load with magnitude equals to the sum of the distributed loads or the product of uniform distributed load per unit area and the applied area, acting on the center of gravity or center of mass, or center of centroid of the applied area of applied load. In general, the magnitude of the equivalent normal concentrated load for the resultant force of a distributed load is equal to the summation of the all distributed forces or the area under the function of the distributed load. And the applying position of the equivalent normal concentrated load can also determined by taking moment about a pont or an axis as in body force. For example, a distribution load of load distribution function, D(x) spread on a beam along x axis, imply 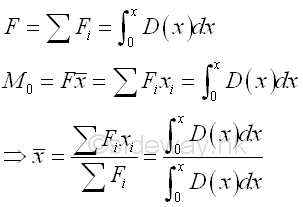
Link:http://output.to/sideway/default.asp?qno=120300018 Knowledge Base FFmpeg InformationReference from FFmpeg Document: http://ffmpeg.org/ffmpeg.html last updated 28Nov2015 Reference from FFmpeg FAQ : http://ffmpeg.org/faq.html last updated 28Nov2015 
source: http://ffmpeg.org/ffmpeg.html 





















source: http://ffmpeg.org/faq.html 







Link:http://output.to/sideway/default.asp?qno=120300019 Batch Conversion Batch Convertion of media filesThe "ffmpeg.exe" file can be used to convert a media file from one type to another. To convert all media files in all subdirectories, one way is to make the converting program "ffmpeg.exe" recursively walking into the directories from the current directory. The following is the batch file for recursively converting:
echo
converting The batch file can be executed by a short-cut with "Target" is the location of the batch file and the "Start in" is the parent directory to be performed convertion.
|
Sideway BICK Blog 28/03 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||