Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway
Sideway
BICK BLOG from Sideway
|
Link:http://output.to/sideway/default.asp?qno=141200003 Mechanics Kinetic Impulse Kinetics: ImpulseWork is the study of the effect of a force along with the displacement of an object. Power is the study of the time rate of doing work. The time required to do work is also a constraint on studying the motion of an object. Impulse is another concept developed to study the effect of the motion of the object acting on another object over a time interval. Principle of Impulse and MomentumBy Newton's Second Law, the acceleration of an object due to the force F acting upon an object is proportional to the magnitude of the force and the acceleration is in the direction of the force. Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity. Since the mass of the object is constant, force can then be expressed in term of the rate of change of the product of mass and velocity. By definition of momentum, the product of mass and velocity is equal to the momentum of the object. In other words, the force F acting upon an object is equal to the rate of change of the momentum of the object. 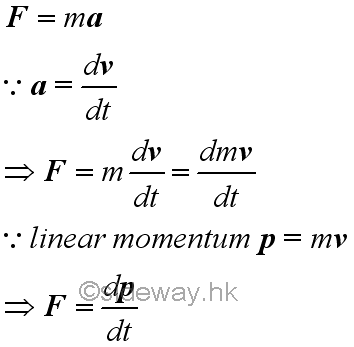
For the kinetic motion of the object, a concept of impulse is defined to quantify the change of kinetic motion of an object after a time interval which is expressed as the vector sum of the applied force acted upon the object over the time interval. 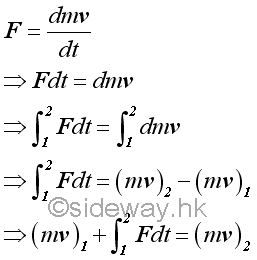
The integral of force with respect to time is a vector quantity call impulse or linear impulse. The linear impulse is therefore equal to the linear momentum change. Although in many applications, an impulse is usually refer to a constanct force acting over a small time interval, an impulse can be applied to any application by performing the integration of the integral of which the force can be a constant force or a function of time. 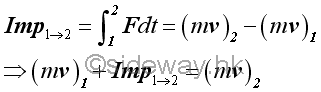
Since impulse is a vector quantity, the final momentum vector of an object is equal to the initial momentum vector of the object plus the impulse vector of the force during the time interval considered vectorially. 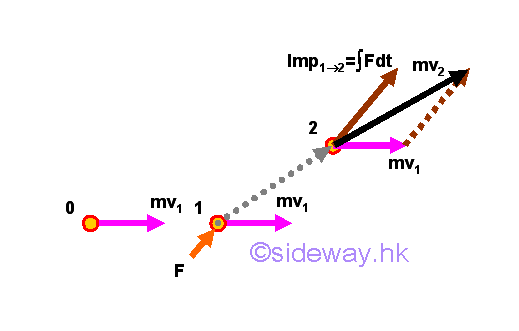
Similarly, the force vector can also be resolved into rectangular componebts, 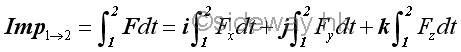
Momentum Change under a Constant Force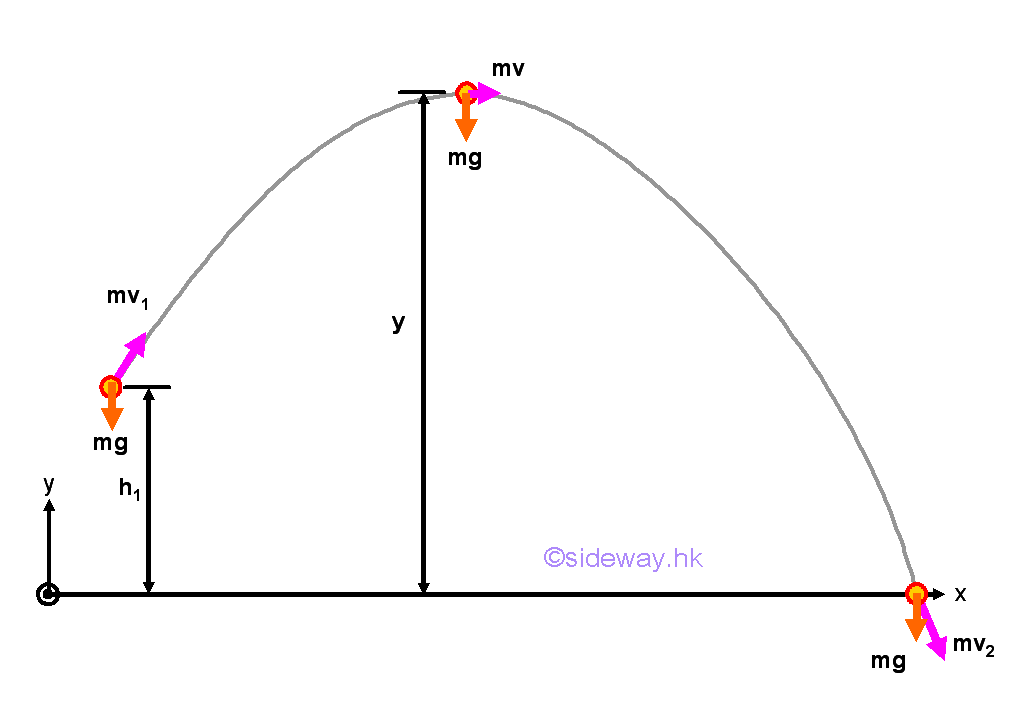
The nature of an impulse is just a force function acting on an object over a time interval. For example, a projectile of mass m projected from a level of height h1 with initial launch velocity v1 and initial launch angle θ under a constant force of gravity over a time interval, the momentum change of the projectile just before hitting the ground can also be determined by means of the principle of impulse and momentum if the time interval is known. The x component of the momentum of the projectile remains unchanged. 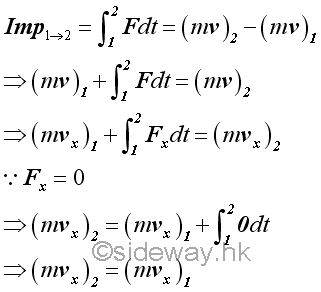
The y component of the momentum change of the projectile can be expressed in form of impulse and momentum change. 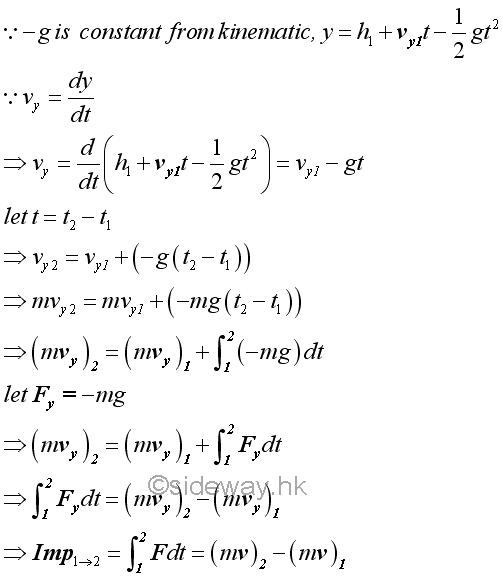
Therefore. 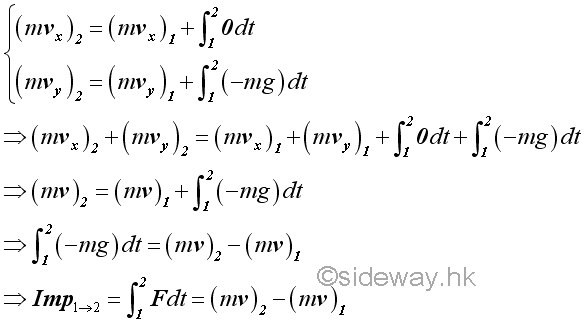
Momentum Change under a Varibale Force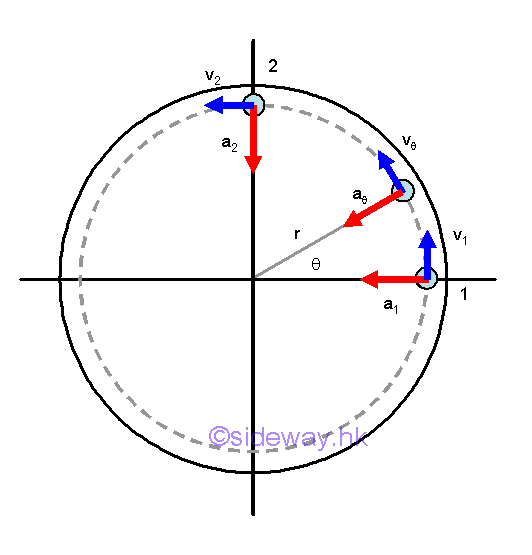
In fact, an impulse can also a variable force function acting on an object over a time interval. For example, a horizontal circular motion of a mass m. the momentum change of the mass can also be determined by means of the principle of impulse and momentum. 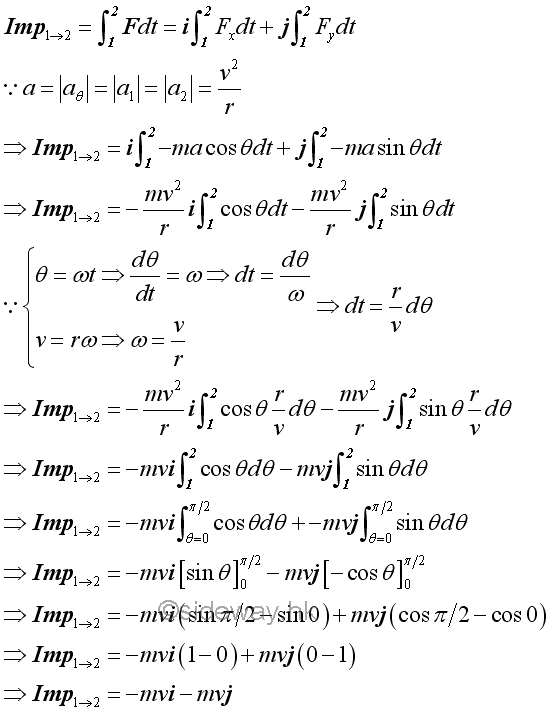
Therefore by the principle of impulse and momentum change, imply. 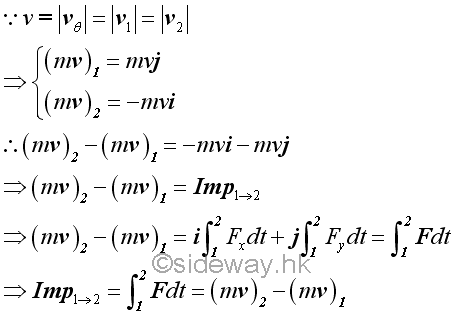
Momentum Change of a System of ObjectsSimilarly, the principle of impulse and momentum change can also be applied to a system of objects by considering each particle separately. 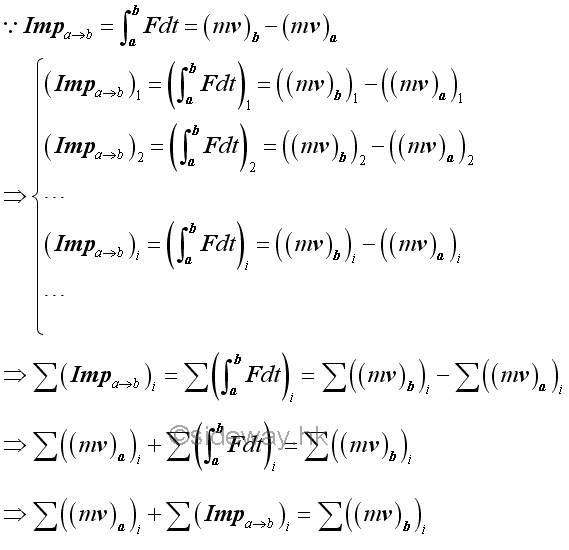
For example, two objects are connected by a spring and are held some distance apart. By neglecting the friction force, the momentum changes of two objects can be related by the principle of impulse and momentum change. 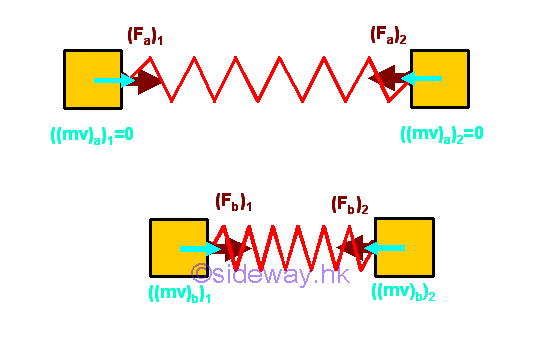
Since the spring forces acting on the two object are always equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, The momentum changes of the two objects can be related by the impulses acting on the two objects. 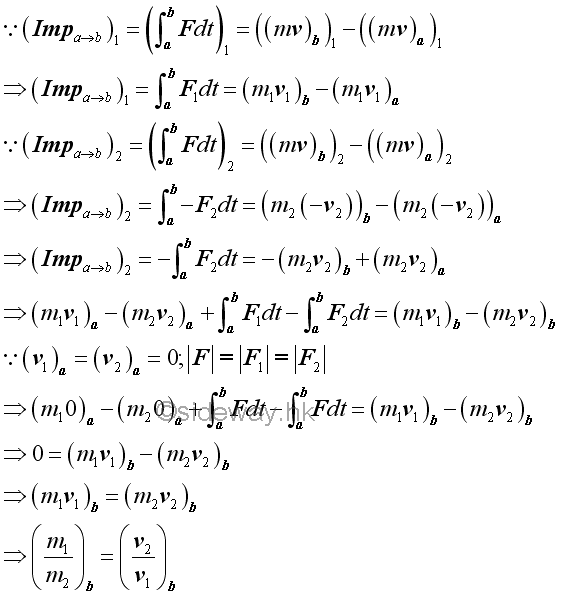
Since there is no external force acting on the system, and the internal forces, spring forces, acting upon the system of objects always form equal and opposite force pairs, the impulse acts on the system must be equal to zero. Therefore the total momentum of the system of objects must always be the same. In other words, the total momentum of the system of objects is conserved. For a two objects system, the velocities of the two objects are inversely proportional to the masses of the two objects. 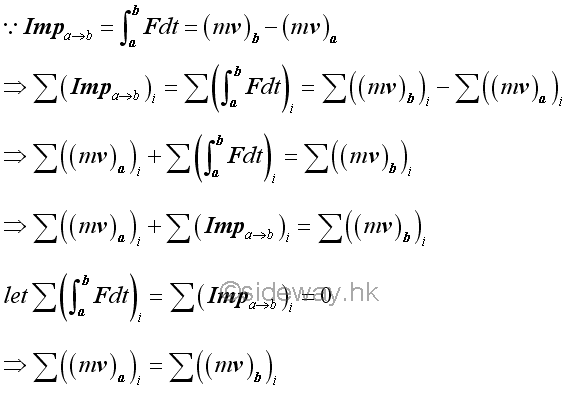
Impulse Motion under an Impulsive ForceThe concept of impulse usually focus on applications of applying a large force to an object over a very short time interval such that a definite momentum change of the object is produced. An impulsive force is therefore a force that can cause a definite momentum change over a very short time interval. And the resulting motion due to an impulsive force is called an impulsive motion. Comparing to an impulsive force, a non-impulsive force usually produces a gradually change in the momentum of the object. Force of gravity acting on a projectile, centripetal force acting on an object undergoing circular motion, or the spring forces acting on a spring connected objects are examples of non-impulsive forces. Since an impulsive force only acting on an object over a very short time interval, the resulting impulse is equal to the average value of the force exerting on the object during the short time interval. 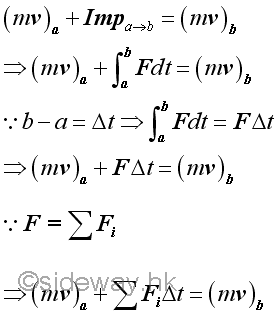
Since the impulsive action usually produces a much larger momentum change than that of the non-impulsive forces produce, the non-impulsive forces acting on an object can usually be neglected in the application of the principle of impulse and momentum. Similarly, the impulsive motion can also be applied to a system of objects. 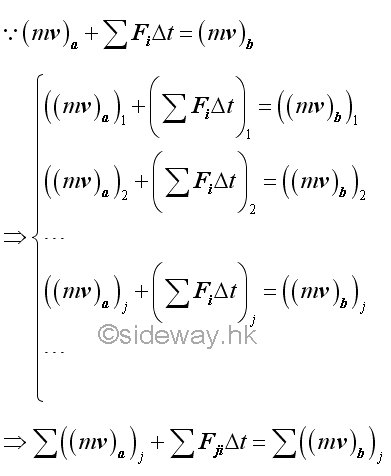
If there is no external impulsive force acting on the system of objects, and all external non-impulsive forces acting on the system of objects can be neglected. The equation of impulse and momentum can be reduced to equation of momentum terms only. Therefore the total momentum of the system of objects must always be the same. In other words, the total momentum of the system of objects is conserved. 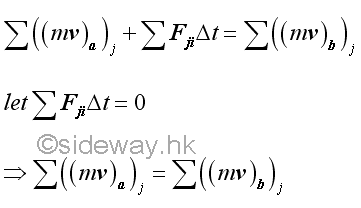
Link:http://output.to/sideway/default.asp?qno=141200002 Mechanics Power Kinetics:In a practical application, besides the total work done or total energy needed to do a job, sometime how fast the work is done or how fast the energy is used is a much more important concern. Work, Energy, and PowerWork is a description of an activity that cause the displacement of an object along with the direction of force applied on. Energy is a concept of the capacity for doing work. Numerically, by the principle of work and energy, the energy processed by the object must have same value to accomplish the corresponding work. Power is defined as the time rate of doing work and therefore numerically the power of doing work has the same value as the power of the time rate of using energy to do the corresponding work. PowerBy definition, the average power of doing work is the total work done that has done during the time interval of doing the work. 
By taking limit as Δt approaching zero, the instantaneous power, or the time rate of doing work at an instantaneous time interval is 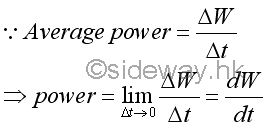
Since work done is defined as the displacement of an object in the direction of force applied on, 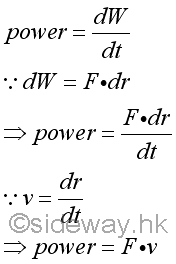
EfficiencyIn practical mechanical problems, friction forces are always involved. Friction force is a non-conservative force depending on the path travelled. Since extra work is needed to overcome the work due to the friction force, the work output of a mechanical device is usually less than the work input to the mechanical device. The mechanical efficiency, b of a mechanical device is defined as the ratio of the output work over the input work to measue the efficiency of a mechanical design for a device or machine. In other words, the efficiency of a mechanical machine is always less than 1. Imply 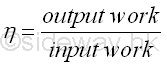
Since the derivation of the efficiency of a mechanical device or machine is based on the work that is done at a constant rate, the efficiency of a mechanical device or machine can also be expressed in term of the rates of output work done and input work done. Imply 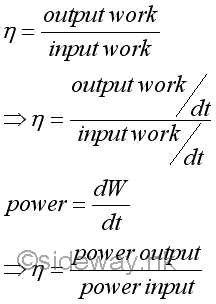
By the principle of conservation of energy, the efficiency of a device can also be applied to device transforming mechanical energy into other forms of energy such as electric energy, thermal energy etc. |
Sideway BICK Blog 09/12 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||